The highest priority with packing systems for medical devices, which are sterilised in the final packing, is the maintenance of the sterility up to application, as well as making the product aseptically available to the patient (DIN EN ISO 11607-1). For this purpose appropriate testing has to be carried out, which enables the development and definition of packing systems and medical devices.
Accelerated ageing
Accelerated ageing of packaging as a simulation of the ageing process to validate the sterile pack and the expiration date (According to DIN EN ISO 11607-1 stability testing can be performed on accelerated aged sterile barrier systems, if no real-time data is available).
Test requirement
Accelerated ageing according to ASTM Standard F 1980 (Accelerated Ageing of Sterile Medical Device Packages)
Test setup
For this method of artificial ageing, the packaging samples are incubated at constant temperature for a defined number of days. For the determination of the constant accelerated ageing temperature (AAT), the material characteristics and the maximum temperatures that would cause product and/or packaging damage have to be determined.
Maximum dimensions of the test specimen: 600x600x1800 mm Duration: not specified
Testing of functional efficiency of sterile packaging, possibly in combination with protective packaging
Visual inspection
In accordance with: ASTM F 1886/1886M (Standard Test Method for Determining Integrity of Seals for Medical Packaging by Visual Inspection)
Test method
The specimens are subjected to a visual inspection before and after accelerated ageing and after the mechanical stress. The specimens are checked with regard to the following irregularities:
- Unsealed areas (in the sealed seam)
- Inhomogeneous, not sufficiently sealed areas
- Too strongly sealed areas
- Constrictions or channels in the seal
- Wrinkles and cracks, holes or flaws in the seal
Maximum dimensions of a test specimen: not specified Duration: 1 day
Mechanical stress of sterilisation packages
In accordance with: ASTM D 6179 (Standard Test Methods for Handling of Unitized Loads and Large Shipping Cases and Crates) and ASTM D 4169 (Standard Practice for Performance Testing of Shipping Containers and Systems)
Test method
Mechanical stress of the test samples by agitating in a drum (diameter 480 mm). This is followed by a visual inspection for any obvious damage, especially in the area of the sealing seams.
Maximum dimensions of the test specimen: 350x350x200 mm Duration: 2 days
Whole Package Challenge Test
Standard Test Method for Microbial Ranking of Porous Packaging Materials, Exposure Chamber Method
According to: ASTM F 1608 which modifications
A method for Evaluating the Microbial Barrier Properties of Intact Packages
Test method
By default, 30 test specimens are tested. They are evenly distributed in the test chamber and contaminated with an aerosol of Bacillus atrophaeus. After the dusting process, the outer surface of the packaging is disinfected. Subsequently, the specimen or package contents are subjected to a sterility test according to ISO 11737-2. For this, the samples are transferred to Tryptic Soy Broth and incubated for 14 days at 30 +/- 2 °C. At the same time or afterwards, growth monitoring of the test micro-organism is carried out. In addition, the following controls are performed:
· Maximum 3 Positive Controls, damaged deliberately before the dusting process.
· 1 Negative Control, which serves to demonstrate the sterility of samples prior to the procedure
Maximum dimensions of the test specimen: 600 x 380×250 mm
Duration: 21 days
Checking of seal seams of sterile packaging
Tensile strength test
In accordance with:
1.) DIN EN 868, Part 5, Appendix D (packaging materials for medical devices to be sterilised in the final packaging – Part 5: Sealable transparent pouches and tubes made of porous material and plastic composite film – Requirements and test methods – Appendix D: Method for determining the strength of the seam in transparent pouches and tubing)
or
2.) DIN EN 868, Part 4, Appendix C (packing materials for medical devices to be sterilised in the final packaging – paper pouches – requirements and testing methods – Appendix C: Procedures for the determination of the tensile strength of the seam of paper pouches produced from a single paper web based on: DIN EN 868, Part 4, Appendix C: packing materials for medical devices to be sterilised in the final packaging – paper pouches – requirements and testing methods – Appendix C: Procedures for the determination of the tensile strength of the seam of paper pouches produced from two paper webs)
Test method
The tensile strength test of the seal seams is determined by means of a tensile testing machine. For this purpose, a total of 20 pieces of 15 mm +/- 0.1mm each are cut out of 10 packages (a sample from the longitudinal seam and from the transverse seam out of the middle of each sample) and then tested (also blank samples)
Maximum dimensions of a test specimen: not specified Duration: 1 day
Peel test
In accordance with: DIN EN 868, Part 5, Appendix E (packaging materials for medical devices to be sterilized in the final packaging – Part 5: Sealable transparent pouches and tubes made of porous material and plastic composite film – Requirements and test methods – Appendix E: Procedure for determining the peel characteristics of paper / plastic – composite materials)
Test method
In order to test the peel characteristics, the seal seams are slowly and carefully taken apart manually in 10 samples. The continuity of the seal seam is checked by visual inspection along the entire length and width of the seal line. The seal seam width is measured on the inner surface of the plastic.
Maximum dimensions of a test specimen: not specified Duration: 1 day
Testing for impermeability and continuity of sealing
In accordance with: DIN EN ISO 11607, Part 1 (packaging for medical devices to be sterilised in the final packaging – part 1: Requirements for materials, sterile barrier systems and packaging systems)
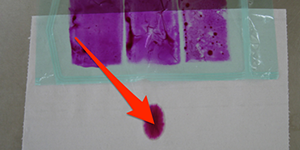
1.) Porous medical packaging in accordance with: ASTM F1929 (Standard Test Method for Detecting Seal Leaks in Porous Medical Packaging by Dye Penetration)
2.) Nonporous medical packaging in accordance with: ASTM F3039 (Standard Test Method for Detecting Leaks in Nonporous Packaging or Flexible Barrier Materials by Dye Penetration)
Test method
For permeable (porous) packing materials: The test is performed in 10 (empty) packages using a toluidine blue test solution. Each package is examined by visual control. The number of evidences of seal failure evidenced by dye penetrating through the seal and the respective location within the packaging is documented. Materials such as paper and Tyvek are considered to be permeable packaging materials (Porous Medical Packaging).
For impermeable (nonporous) packing materials: The test is performed on 10 (empty) packages using toluidine blue dye solution. Each package is examined by visual control. The number of evidences of seal failure evidenced by dye penetrating through the seal and the respective location within the packaging is documented. If the packaging materials tested are not translucent, the outer side of the sealed seam is brought into contact with white filter paper for 5 seconds and afterwards checked for discoloration as a result of any impermeableness of the sealing seam. Many plastics such as PE, PA, aluminium, etc. are considered to be impermeable packaging materials (nonporous medical packaging).
Maximum dimensions of a test specimen: not specified Duration: 1 day
Determination of fine holes in the plastic composite film
In accordance with: DIN EN 868, Part 5, Appendix C (Packaging materials for medical devices to be sterilised in the final packaging – Part 5: Sealable transparent pouches and tubes made of porous material and plastic composite film – Requirements and test methods – Appendix D: Method for determination of fine holes in the plastic composite film).
10 film samples are individually tested in succession. For this purpose, the inner surface of each sample is placed on filter paper. Then a sponge with riveted steel plate is transferred into the dye solution for 1 minute. The sponge remains on the sample for 2 minutes. After removal of the sponge, the filter paper is examined for discoloration as a result of damage to the foil.
Maximum dimensions of a test specimen: not specified Duration: 1 day
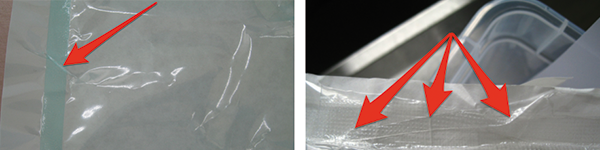
Determination of peel characteristics
Paper / plastic – composite materials according to DIN EN 868-5:
Irregular sealing,
insufficiently sealed area

Paper fibre removal when opening the seal
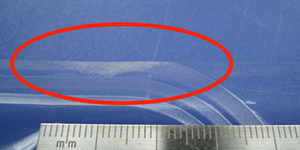
Typical discoloration of the paper / uneven peeling performance

Testing of tightness and continuity of the seal, as well as determination of fine holes in plastic composite film
In accordance with ASTM F1929 as well as ASTM F3039 and according to DIN EN 868-5:
Determination of the fault in the seam due to the fold
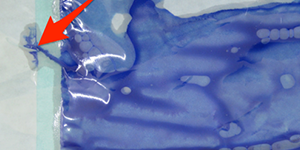
Colour solution applied with a sponge

Detected leak / leaking control fluid